10 Amazing Facts About the English Tarantula
The English tarantula, a fascinating creature shrouded in both intrigue and misconception, has captured the attention of arachnid enthusiasts worldwide. Often misunderstood due to their intimidating appearance, these spiders possess a unique set of characteristics. This article will delve into 10 amazing facts, dispelling myths and revealing the wonders of these often-overlooked animals. Prepare to be amazed as we explore their physical attributes, habitats, behaviors, and their role in the ecosystem. From their remarkable hunting skills to their often misunderstood venom, we’ll uncover the secrets of the English tarantula, offering a new appreciation for these captivating creatures. The following facts aim to illuminate the world of these magnificent arachnids.
Appearance and Characteristics
English tarantulas, like all tarantulas, are easily recognizable by their hairy bodies, eight legs, and two body segments cephalothorax and abdomen. Their size can vary greatly depending on the species, but generally, they are quite large spiders. Their physical appearance is a key aspect of their identity, setting them apart from other arachnids. The coloration, the presence of urticating hairs, and other morphological features are all important characteristics to understand.
Size and Physical Traits
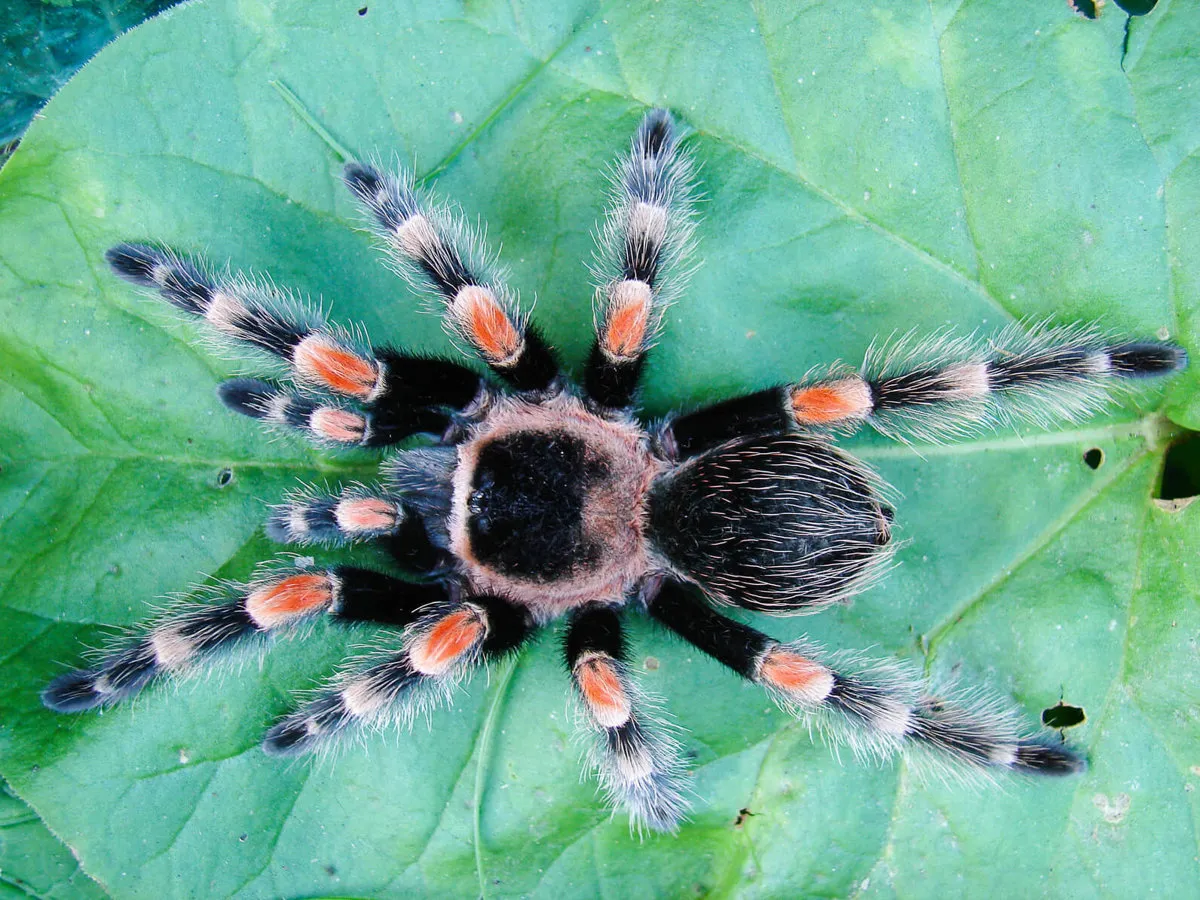

The size of an English tarantula can be a significant factor in its appeal, as well as its behavior. They typically range from a few inches to several inches in leg span. The males are often smaller and have longer legs compared to the females. The presence of fangs, the shape of the cephalothorax, and the arrangement of the eyes are other physical traits that distinguish tarantulas from other spiders. The size is also determined by factors such as age, food availability, and genetics.
Color Variations
The coloration of English tarantulas is incredibly diverse, providing both camouflage and, in some species, a warning to potential predators. Colors can range from earthy browns and blacks to vibrant blues, oranges, and reds, depending on the species and sometimes the individual. These colors are often the result of pigments found in the exoskeleton, or the arrangement of microscopic structures that reflect light. The patterns and colors can also be used as a method of attracting mates, or for camouflage in the environment. The molting process can also reveal brighter colors, as a new exoskeleton is formed.
Habitat and Distribution
Understanding the habitat and distribution of English tarantulas is crucial to appreciating their ecological role. They are found in diverse environments, adapting to a variety of climates and terrains. The habitats they occupy are fundamental to their survival, providing shelter, prey, and the right conditions for reproduction. The distribution of tarantulas across the globe is influenced by factors like climate, food availability, and the presence of predators. Their adaptability is what enables them to colonize diverse areas.
Natural Environment
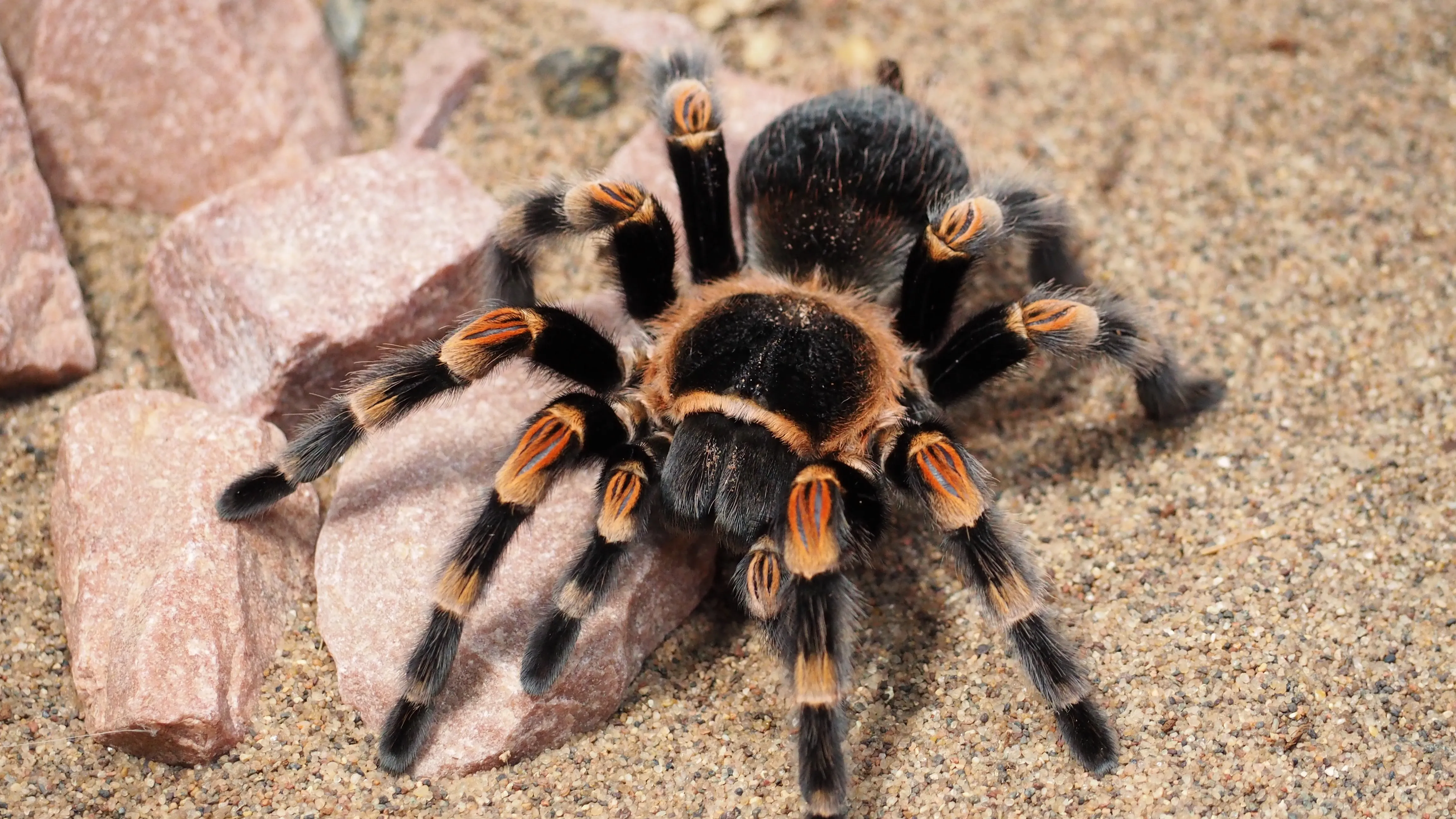

English tarantulas thrive in a variety of natural environments, typically favoring warm, humid climates. These spiders often live in burrows, under rocks, or among leaf litter, providing shelter from predators and extreme temperatures. The composition of the soil and the availability of water also play a crucial role in their habitat. The specific environmental conditions influence their behavior, including their hunting patterns and reproductive cycles. The presence of specific vegetation and other animals also contributes to the overall habitat.
Geographical Range
The geographical range of the English tarantula depends on the species. While ‘English tarantula’ isn’t a specific recognized species, it refers to tarantulas found in certain regions. They are often found in regions with favorable climates and the availability of resources, from desert regions to tropical forests. Understanding their geographical distribution is also critical for conservation efforts, helping to identify vulnerable populations and protect their habitats. Their ability to adapt to different environments is a testament to their resilience.
Behavior and Lifestyle
The behavior and lifestyle of English tarantulas are incredibly diverse. These arachnids exhibit a range of fascinating behaviors that are vital for their survival. The way they hunt, build webs, and interact with their environment reveals much about their capabilities. Studying their lifestyle not only increases our knowledge but also helps us understand their role in the ecosystem and their adaptability.
Hunting and Feeding Habits
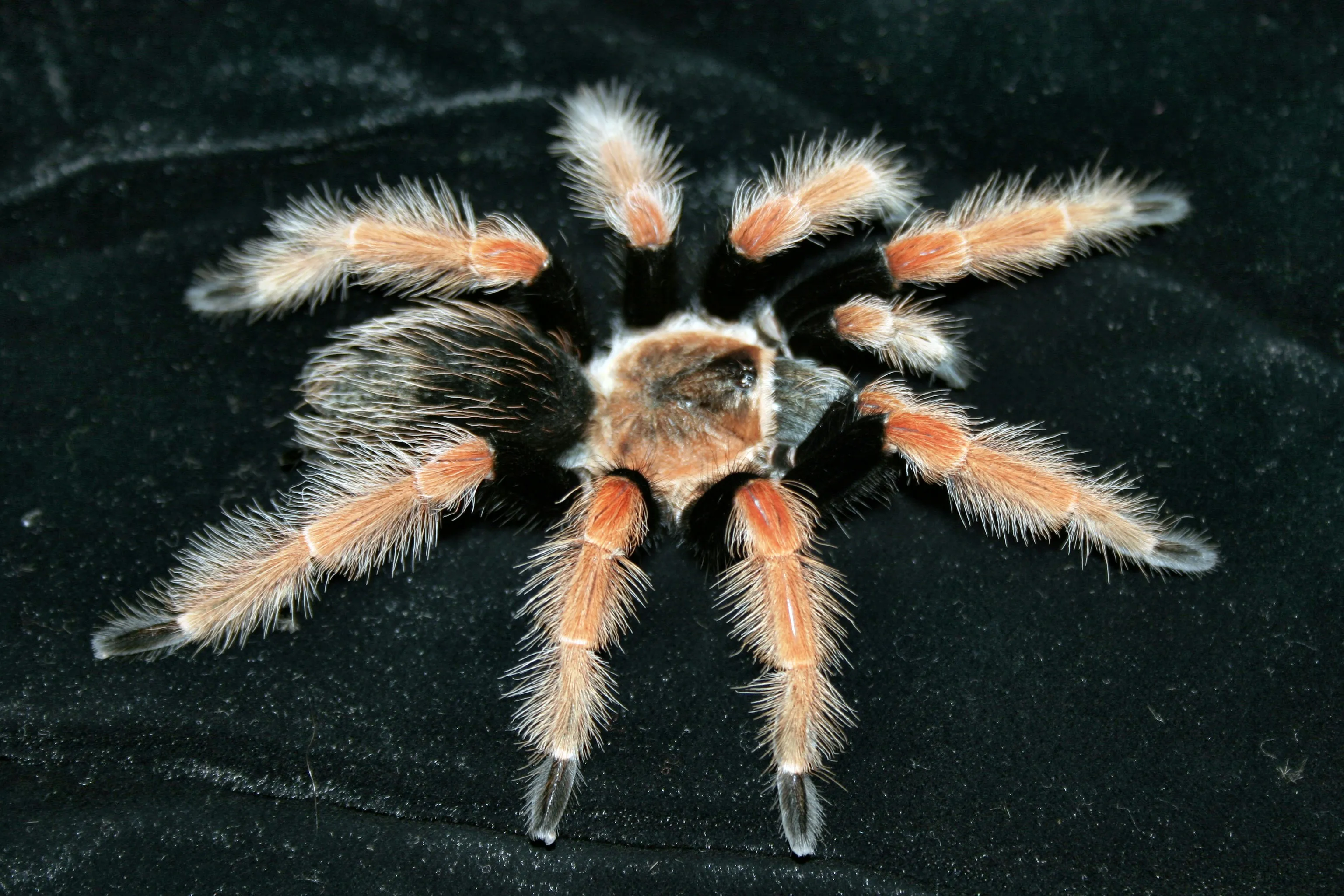

English tarantulas are primarily predators, with their diet consisting of insects, small vertebrates, and other invertebrates. They are ambush predators, waiting patiently for prey to come within striking distance. Some species hunt from burrows, while others actively search for their food. The hunting strategy and food preferences vary among species, influenced by factors such as habitat and prey availability. Their venom helps immobilize their prey, making it easier for the spider to consume.
Web-Spinning and Shelter
Although not all tarantulas are web-builders, many utilize silk for shelter and protection. They create silk-lined burrows or retreats, using silk to reinforce their homes. The silk also serves as a way to detect vibrations, alerting the tarantula to the presence of prey or potential threats. The way they build and use their shelters is intricately linked to their survival. They might line their burrows with silk to create a safe environment from predators.
Lifespan and Reproduction
The life cycle and reproductive behaviors of English tarantulas offer fascinating insights into their biological adaptations. Understanding these processes provides essential information about their conservation and their population dynamics. Their longevity, reproductive strategies, and mating rituals show the complexity of their biological systems.
Life Cycle

The life cycle of an English tarantula involves several stages, starting from the egg sac to the adult form. They undergo molting, shedding their exoskeleton as they grow. The duration of the life cycle can vary among species. Males often have shorter lifespans than females. Environmental factors, such as temperature and food availability, also influence their growth and development.
Mating Rituals
Mating rituals are a critical part of the tarantula’s life cycle. Males often initiate courtship by drumming on the ground or displaying specific behaviors to attract the females. After mating, the female lays eggs, which are then enclosed in an egg sac. The male’s approach can sometimes be dangerous as the female might attack him. The complexity of mating rituals is crucial for successful reproduction and species continuation.
Venom and Defense Mechanisms
The venom and defense mechanisms of the English tarantula are both intriguing and essential for survival. The venom helps in subduing prey, and their defense tactics are key to avoiding predators. Understanding their defensive adaptations highlights their resilience in the face of threats and provides insight into their evolutionary strategies.
Effect of Venom
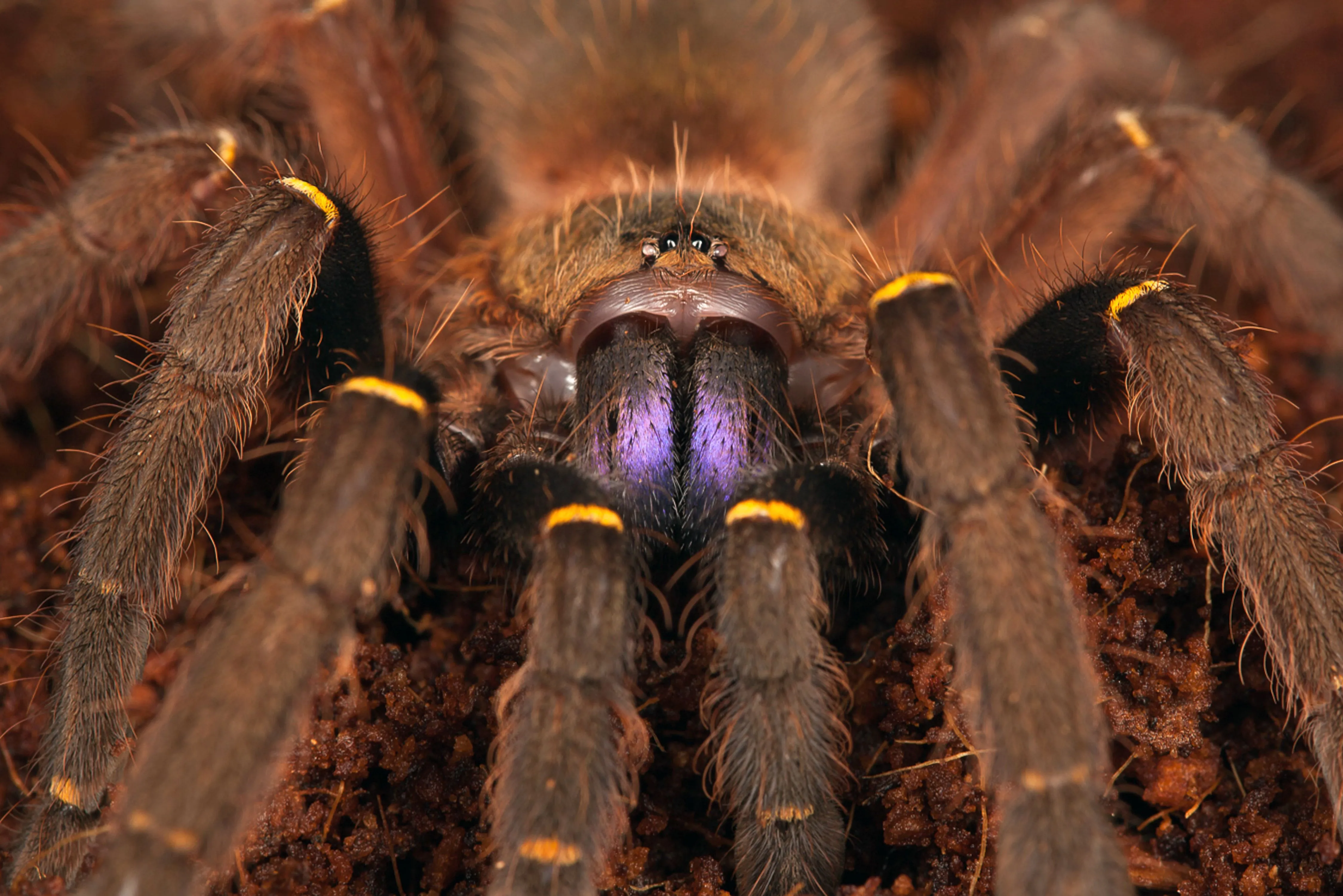

The venom of English tarantulas is primarily used for subduing prey, containing neurotoxins and other components. The effect of the venom on humans is usually mild, causing localized pain, but in rare cases, there might be more severe reactions. The toxicity varies among different species. The venom also helps the spider pre-digest its prey. Despite their venom, tarantulas aren’t typically considered highly dangerous to humans.
Defense Techniques
English tarantulas have evolved a variety of defense techniques to protect themselves from predators. These include flicking urticating hairs, which can cause irritation, as well as biting. They might also try to flee or hide in their burrows. These defense mechanisms provide protection from various threats in their natural habitat. Their first line of defense usually involves trying to escape or bluffing.
Popularity as Pets
English tarantulas have gained popularity as pets, attracting individuals with an interest in unique creatures. Their relatively low-maintenance requirements and interesting behaviors contribute to their appeal as companions. Owning a tarantula, however, comes with significant responsibilities, requiring owners to understand their needs and provide proper care. Their increasing popularity has led to increased awareness and information about their care.
Responsible Ownership

Responsible ownership of an English tarantula includes providing appropriate housing, a balanced diet, and a suitable environment. Owners must ensure the tarantula’s safety and health, as well as their own safety. Proper handling techniques and knowledge about their behavior are vital for a safe and enjoyable experience. This also means being prepared for potential health issues and providing the necessary care.
Ethical Considerations
Ethical considerations in tarantula ownership involve sourcing them from reputable breeders and ensuring their welfare. It is essential to avoid contributing to the illegal wildlife trade and to prioritize the spider’s well-being. Responsible pet ownership includes providing enrichment, avoiding stress, and educating oneself on their natural behaviors and needs. This also includes understanding that these are wild animals.
Conservation Status
The conservation status of English tarantulas highlights the threats they face in their natural habitats and the efforts being made to protect them. Understanding the conservation status is essential for implementing effective strategies for their preservation. Monitoring their populations and addressing the challenges they encounter ensures their survival.
Threats to Survival
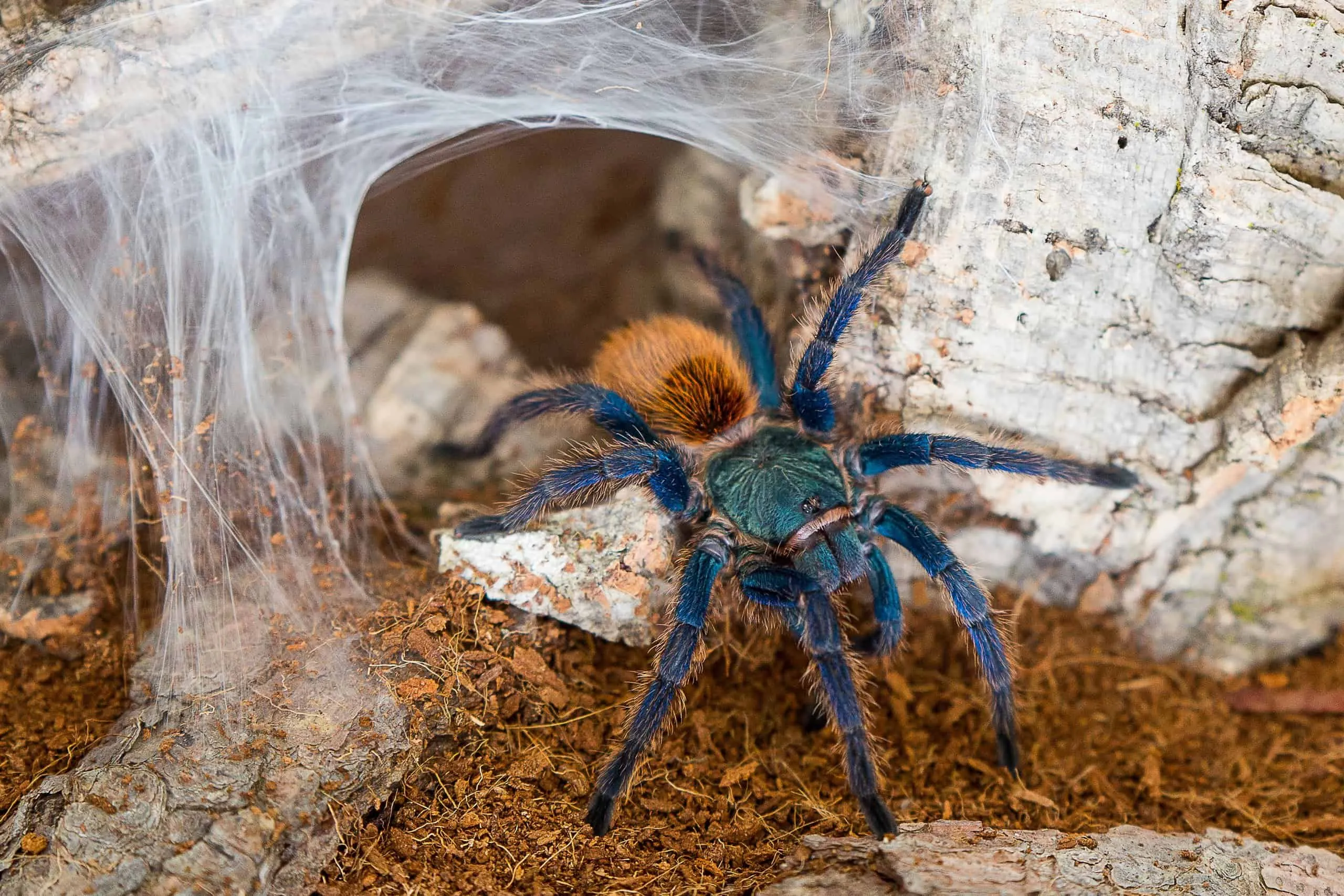

English tarantulas face several threats to their survival, including habitat loss, the impact of climate change, and illegal collecting. These threats can lead to population declines and jeopardize their long-term survival. Understanding these threats helps in devising effective conservation strategies. Destruction of their natural habitat can result in severe reductions in their population.
Conservation Efforts
Conservation efforts for English tarantulas include habitat protection, breeding programs, and raising public awareness. Organizations and individuals are working to protect their natural environments and populations. These efforts are crucial for the conservation of biodiversity and ensuring the long-term survival of these remarkable creatures. Supporting research, education, and sustainable practices contribute to their conservation.
Conclusion
The English tarantula, with its fascinating characteristics and behaviors, is a creature deserving of our respect and admiration. The ten amazing facts revealed in this article only scratch the surface of what makes these spiders so unique. Whether you are a seasoned arachnid enthusiast or a curious newcomer, the English tarantula is sure to leave a lasting impression. By understanding their significance in the ecosystem and the challenges they face, we can become better stewards of our planet and ensure that these captivating creatures continue to thrive for generations to come.